
 English
English
Information Center
Intelligent and environmentally friendly aluminum for future construction

 English
English
Intelligent and environmentally friendly aluminum for future construction
In September 2013, the State Council issued the "Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan" plan, which became a guiding document for air pollution prevention and control in the future. In July 2016, with the approval of the State Council, the Chinese Academy of Engineering and the Ministry of Environmental Protection released a mid-term evaluation report on the implementation of the "Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan". The assessment concluded that: Although the improvement of air quality has been effective, the situation is still severe, the problem of heavy pollution in winter is prominent, and the annual average concentration of PM10 in individual provinces has increased. Beijing needs to make greater efforts to achieve the end-of-2017 target. In 2017, the state paid special attention to environmental governance, especially the pollutant emissions in Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei and surrounding areas. It controlled environmental pollution through various policies to ensure the completion of the goals of the "Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan". On January 31, 2018, the Ministry of Environmental Protection said at its press conference that the goals of the Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan have been fully achieved, and a three-year plan to win the blue sky defense war will be formulated and implemented in the future.
In 2017, in addition to imposing winter production restrictions on "2 + 26" cities located in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei air pollution transmission channel, the state also proposed to implement special emission limit standards for industrial pollutant emissions and carry out unorganized emission control. The aluminum industry has been included in key control industries in the region, and environmental protection governance is facing unprecedented challenges.
Winter production limit
2017 is the final year of the first phase of the Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan. In order to actively promote the specific implementation of the Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan, at the beginning of 2017, the Ministry of Environmental Protection issued the "Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and surrounding areas 2017 Air Pollution Prevention and Control Work Plan" (Huantiao [2017] No. 29). The governance requirements for the aluminum industry are: during the heating season, the electrolytic aluminum plant has a production limit of more than 30%, based on the number of electrolyzers that have stopped production; the alumina enterprise has a production limit of about 30%, based on the production line; if the carbon enterprise fails to reach the special emission limit, all production will be suspended, and if the special emission limit is reached, the production limit will be more than 50%, based on the production line.
部分地区执行特别排放限值标准
After the implementation of special emission limit standards for pollutants for carbon enterprises, the Ministry of Environmental Protection issued the "Announcement on the Implementation of Special Emission Limits for Air Pollutants in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and Surrounding Areas (exposure draft) " in May 2017, hereinafter referred to as the "exposure draft", which plans to implement special emission limits in the "2 + 26" area. After the "exposure draft" was revised and improved, the Ministry of Environmental Protection officially issued the "Announcement on the Implementation of Special Emission Limits for Air Pollutants in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Air Pollution Transmission Channel Cities" in January 2018, deciding to implement special emission limits for air pollutants in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Air Pollution Transmission Channel Cities. The specific regulations involved in the aluminum industry are: (1) Implementation area: Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei air pollution transmission channel cities include Beijing, Tianjin, Shijiazhuang, Tangshan, Langfang, Baoding, Cangzhou, Hengshui, Xingtai, Handan City, Taiyuan, Yangquan, Changzhi, Jincheng City, Jinan, Zibo, Jining, Dezhou, Liaocheng, Binzhou, Heze City, Shandong Province, Zhengzhou, Kaifeng, Anyang, Hebi, Xinxiang, Jiaozuo, Puyang City (referred to as "2 + 26" cities, including Hebei Xiongan New District, Xinji City, Dingzhou City, Henan Gongyi City, Lankao County, Huaxian County, Changyuan County, Zhengzhou Airport District). ( 2) New projects: For industries and boilers that have specified special emission limits for air pollutants in the national emission standards, from March 1, 2018, the construction projects newly accepted for EIA will implement special emission limits for air pollutants. (3) Existing enterprises: thermal power, iron and steel, petrochemical, chemical, non-ferrous (excluding alumina), existing enterprises in the cement industry and in-use boilers, from October 1, 2018, the implementation of special emission limits for sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter and volatile organic compounds. Compared with the "exposure draft", the biggest change in the official announcement is: among the existing enterprises that implement special emission limits, alumina enterprises are not included.
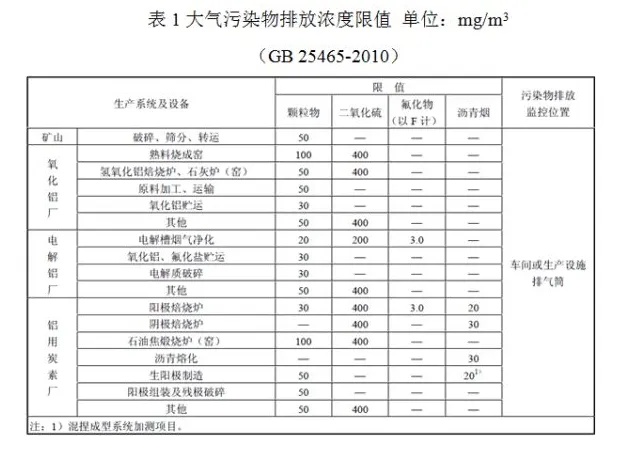
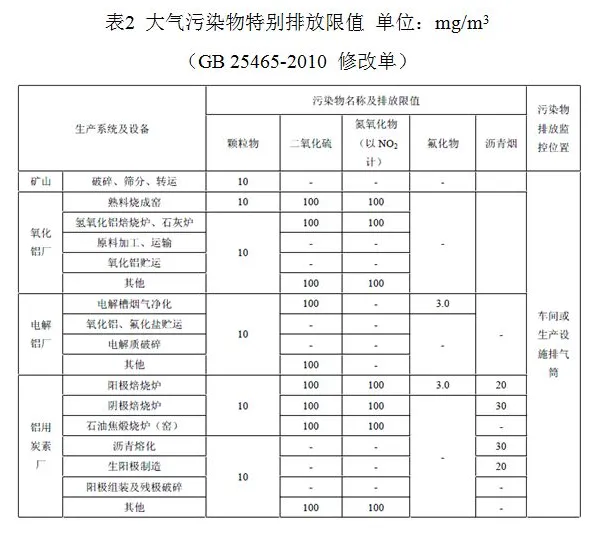
The special emission limits for air pollutants in the aluminum industry have been added to the "Aluminum Industry Pollutant Emission Standards" (GB 25465-2010) in the form of a "modification order" in 2013. Comparing the emission limits and special emission limits, it can be seen that from mines, alumina, electrolytic aluminum, to aluminum-used carbon, the entire upstream of the aluminum industry has stricter emission requirements. The emission concentration of particulate matter will be reduced from 20 to 100mg/m3 to 10mg/m3; the emission concentration of sulfur dioxide will be reduced from 200 to 400mg/m3 to 100mg/m3; the emission requirement of nitrogen oxides for alumina plants and aluminum-used carbon plants is 100mg/m3. Undoubtedly, the implementation of special emission limits has made the aluminum industry face higher environmental protection requirements and greater challenges.
It is understood that the use of desulfurization and denitrification technologies in the production of electrolytic aluminum can meet the requirements of specific emission limits. Among them, the desulfurization technology adopts wet desulfurization, such as limestone-gypsum method; the aluminum oxide denitrification technology can use selective catalytic reduction, dry non-catalytic reduction technology, etc. The investment of desulfurization and denitrification related equipment is expensive. The desulfurization facilities of a medium-sized electrolytic aluminum plant will cost hundreds of millions of yuan and the cost is relatively high, so few companies own these equipment. However, with the implementation of the special emission limit policy, some aluminum companies have begun to upgrade the emission technology of electrolytic aluminum, such as Weiqiao and Chinalco. Among them, the Weiqiao 600kA production line "limestone-gypsum" desulfurization pilot project can make particulate matter ≤ 5 mg/m3, sulfur dioxide ≤ 35 mg/m3, and fluoride ≤ 2 mg/m3. In addition, although the "Announcement on the Implementation of Special Emission Limits for Air Pollutants in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Air Pollution Transmission Channel Cities" does not require alumina companies to implement special emission limits, with the increase in environmental protection efforts, it is not ruled out that alumina companies will also be included in the process of future policy implementation.
Special emission values place very high emission requirements on related aluminum enterprises, so the introduction of equipment such as desulfurization and denitrification will surely be a development trend in the aluminum industry, and the aluminum industry will also face greater environmental challenges!
Unorganized emission control
Unorganized emissions are an important source of air pollution. Due to their many and scattered emissions, they have always been a weak link in environmental governance. In order to further improve the national pollutant emission standards and detail the control measures for unorganized emissions, the Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China has decided to modify the "Aluminum Industry Pollutant Emission Standards" (GB 25465-2010), and at the same time modify the "Recycled Copper, Aluminum, Lead, and Zinc Industry Pollutant Emission Standards" (GB31574-2015), all of which have added "unorganized emission control measures". On June 13, 2017, the Ministry of Environmental Protection released the exposure draft of the standard modification sheet in the form of an announcement, and completed the collection of opinions before June 22. According to the requirements, the unorganized emission control measures for new projects will be implemented from the date of issuance of the amendment order; existing enterprises will be given an appropriate transition period, and the unorganized emission control measures will be implemented from January 1, 2019. The new emission standards have been implemented in advance in aluminum mines, alumina plants, electrolytic aluminum plants, recycled aluminum plants and other enterprises in the "2 + 26" urban area of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei since October 1, 2017.
The unorganized emission of particulate matter in the aluminum industry focuses on mine mining, alumina production, electrolytic aluminum production, etc., followed by material storage and transportation. Specific includes: 1. Aluminum mines: The unorganized emission sources of aluminum ore open-pit mining are perforation dust, blasting dust, shovel dust and coarse crushing station dust. The unorganized emission sources of aluminum ore underground mining are dust generated by rock drilling, blasting, shovel loading and other processes. The unorganized emission sources of concentrators are mainly dust from ore yards, waste rock yards and dump yards, and dust is generated at the receiving point and unloading point of mines, crushers, vibrating screens, and belt conveyors. 2. Alumina production: Alumina production of unorganized emissions are mainly generated in raw materials storage, preparation, clinker crushing, alumina storage and transportation, clinker firing kiln, aluminum hydroxide roasting, molten salt heating, lime furnace (kiln) and other processes as well as red mud yard. 3. Electrolytic aluminum production: Alumina production of unorganized emissions are mainly generated in the preparation of materials, electrolyte crushing, anode assembly and residual treatment, mixing furnace, electrolytic cell and other processes. 4. Material transportation, loading and unloading, storage: In-plant powder material transportation, bulk material transfer, transportation and transfer point, blanking point, etc. will produce particulate matter unorganized emissions.
Although the concretization of unorganized emission management tasks has enhanced the guidance of policies for enterprises and the effectiveness of environmental supervision, there are still certain difficulties in the implementation and supervision of relevant departments due to the large number of unorganized emission sources and irregular emissions. At the same time, the investment in dust removal facilities has undoubtedly increased the operating costs of enterprises, which has also weakened the confidence of enterprises in strictly controlling unorganized emissions.
Up to now, the relevant state departments have not yet issued a policy on limiting production in the 2018 heating season, but some provinces have begun to act in advance. In February 2018, the Henan Provincial Government issued the "Henan Province 2018 Air Pollution Prevention and Control Tough Battle Implementation Plan", requiring: (1) From October 1, 2018, Henan electrolytic aluminum and recycled aluminum will fully implement the national special emission limit regulations for air pollutants. (2) In the 2018 heating season, the province's electrolytic aluminum and alumina enterprises will implement a production limit of more than 30%; carbon enterprises will be suspended; and the melting and casting process of non-ferrous metal recycling enterprises will be limited by more than 50%. ( 3) For electrolytic aluminum enterprises that have reached the special emission limit steadily before the end of October 2018, exempt their staggered production limit ratio from being reduced to 10%, but they must participate in pollution control according to the requirements of the local heavy pollution weather emergency plan; for carbon enterprises that have reached the ultra-low emission limit steadily before the end of October 2018, exempt them from being suspended to limited production by 50%, but they must participate in pollution control according to the requirements of the local heavy pollution weather emergency plan. (4) Fully verify the completion of unorganized emission control in key industrial enterprises. By the end of August 2018, complete the unorganized emission control work in steel, building materials, non-ferrous metals, thermal power, coking and other industries and boilers.
The implementation of special emission limits and the control of unorganized emissions have made aluminum companies, especially those in the "2 + 26" region, face stricter environmental protection requirements, which is both a new transformation and a greater challenge for China's aluminum industry!